Tiny robots, barely perceptible to the human eye, will be able to travel through the bloodstream to cure such lethal and aggressive diseases as cancer. But they will also act on neurodegenerative diseases, hormone deficiencies, and infections. This decade will be key.
The North American film Innerspace premièred 36 years ago. Its protagonist was a pilot who volunteered to be miniaturized in a capsule that was going be injected in the body of a rabbit. The bad guys interfered, and he ended up in a human body. A large part of the film takes place there, among the blood vessels. While science has yet to miniaturize a person, it has managed to manufacture robots that are small enough to travel through our body.
The arrival of minuscule robots —called nanobots— that are capable of travelling through the blood to cure deadly illnesses is about to become a reality. What would seem to be an affirmation of science fiction or a far-off future has ceased to be so. The hope of this great advance for medicine and for health was brought by Jean-Pierre Sauvage, the 2016 Nobel Prize winner in Chemistry for his work on “molecular machines”. The French researcher sewed the seeds of optimism in an interview in the Spanish newspaper El País, where he affirmed that “they are already working on machines that travel through the blood and kill cancer”.
What are nanobots and how do they work?
Nanobots are extremely small functional devices measuring between 0.1 and 100 nm (a nanometer is one billionth of a meter and cannot be seen with a conventional laboratory microscope), and they “enable efficient propulsion through chemical reactions or external physical fields, including ultrasonic, optical, magnetic, and other external fields, as well as microorganisms”, as defined in the academic article, Micro/Nanorobots for Medical Diagnosis and Disease Treatment.
In comparison with conventional robots, nanobots can perform various tasks at the nanometric scale, which has the advantages of high precision, strong flexibility, and wide adaptability, according to the authors of that article. Moreover, these robots can also perform tasks together. The design and development of nanobots will have to be linked to the integration of surface functionalization, remote drive systems, and image tracking technology for medical applications in organisms.
As to the capabilities of these small, remote-control operated machines, they are expected to achieve a much more efficient diagnosis of illnesses in order to apply local and accurate treatment.
Advances for health
To begin to see the potential advances of nanobots, the article, Nanomedicine: Promising Tiny Machine for the Healthcare in Future-A Review, published in the US National Library of Medicine, mentions the great contribution in the fight against cancer. “Nanobots can scan each of the body’s cells for cancerous tendencies, and subject any suspicious cells to careful analysis. If a cancer is detected, they can wipe it out quickly, using more focused and vigorous tactics than the immune system is designed for”, the article states.
Nanobots will also have an impact on all neurodegenerative diseases and those related to the brain, where they could create artificial neural nets “to replace missing neurons and retain old memories”, the experts assure.
And these are not the only fields of action. Nanobots can improve hormone deficiencies to prevent aging or, in the case of infections, clean the body after an illness. Finally, their utility for regenerating the body after an accident and for improving the cardiovascular system is also mentioned.
The future, our best investment
Capitalize on opportunities in a way that is positive, conscientious and committed, with solutions designed for you by our investment experts in your bank in Switzerland.
When will they be a reality?
The medical consensus and researchers indicate that it will take approximately 10 years before seeing nanobots in the first medical applications. Currently, and according to IFL Science, DNA robots are already being tested on animals to search for and destroy cancer cells. Their landing in the health of humans could be a reality within the next decade.
A market that doesn’t cease to grow
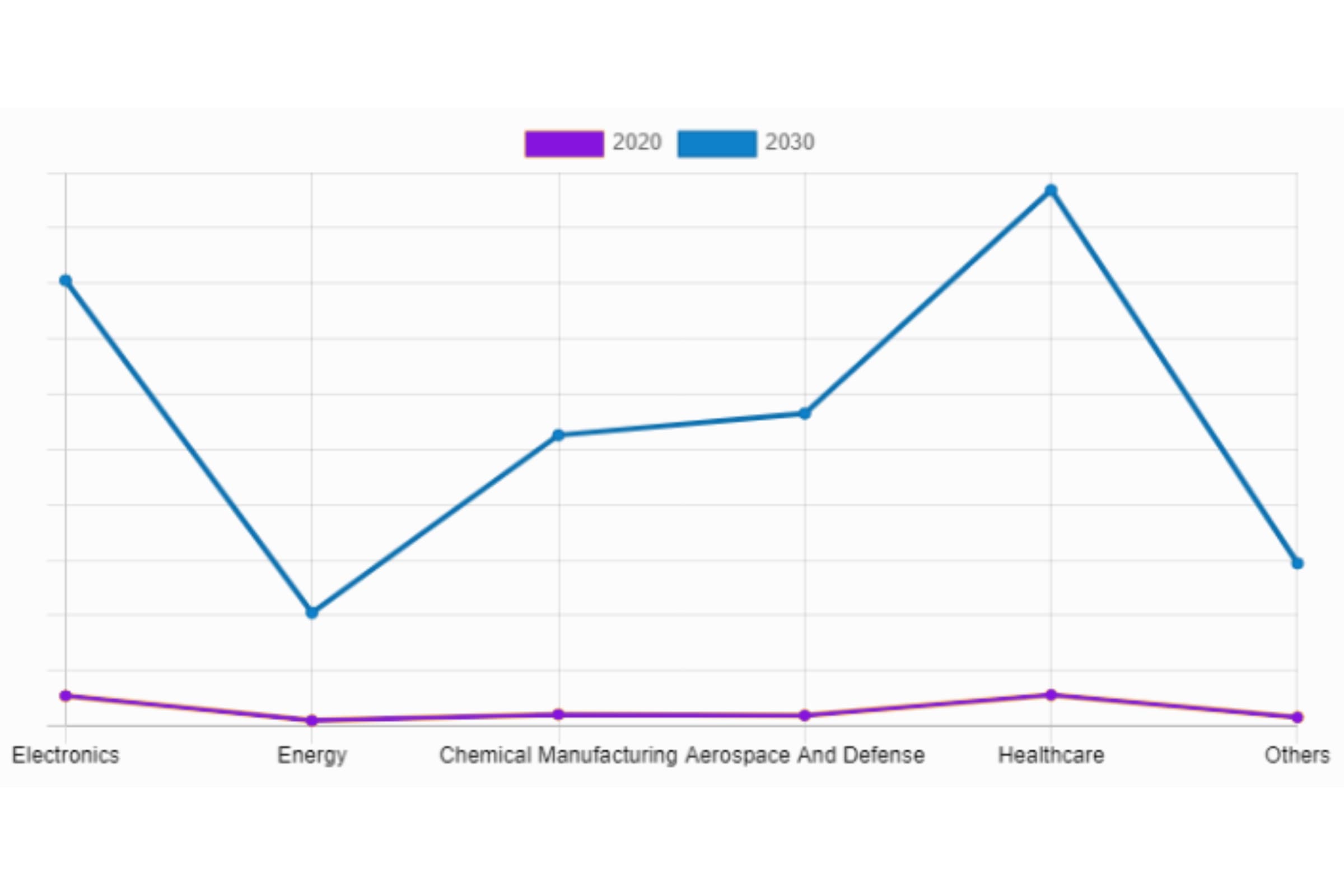
According to a report from Allied Market Research, the global nanotechnology market reached a value of over 1.7 billion dollars in 2020, and it is expected to surpass 33 billion in 2030, which represents an annual growth rate of over 36%. This growth is driven mainly by the development of nanosciences in the medical sector.
Other sources forecast that the market of nanorobotics will exceed 14 billion dollars by 2029, with a growth rate of 10%. Whatever it may be, the good health of this sector doesn’t merely involve applications related to administering medicine, an accurate diagnosis, or the regeneration of tissue. The electronics industry and sectors focused on sustainability and environmental protection are also very interested in nano-scale technologies.
Nanotechnology Market by application. CAGR of 36.4% from 2021 to 2030.