Bitcoin has proven to be a secure and cyberattack resistant network. However, the storage of cryptocurrencies in virtual wallets and exchanges might become vulnerable. In 2021 alone, the theft of cryptocurrencies resulted in a loss of $14 billion for millions of users worldwide.
Bitcoin’s blockchain technology has never been hacked and has emerged as one of the world’s most secure technologies. However, this does not mean that holding bitcoin is risk-free. In fact, unless you have adequate security in place, your wallet could potentially be breached and your cryptocurrency stolen.
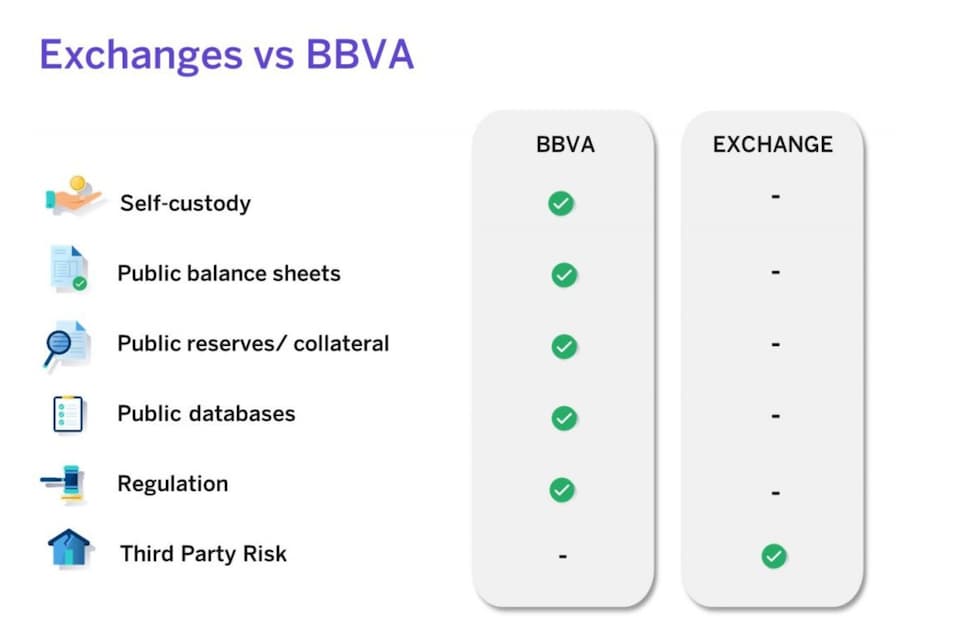
One aspect is the functioning of the Bitcoin network, which has never been hacked, and another is the storage of cryptocurrencies. When we acquire a token of Bitcoin, Ethereum or any other cryptocurrency, we store it in a virtual (or hot) wallet, or in an exchange or a highly secure digital wallet that does not require an internet connection (a cold wallet). It is precisely in the way we store our cryptocurrencies where vulnerabilities can arise, allowing hackers to access our accounts and steal the cryptocurrencies we have purchased.
Investing is more than money
Take part in the most innovative investment trends that matter to you most with your digital account in Switzerland, from 10 thousand dollars, francs or euros.